Research Highlights
Tsinghua Astronomers found the correlation between stellar metallicities and planet mutual inclinations
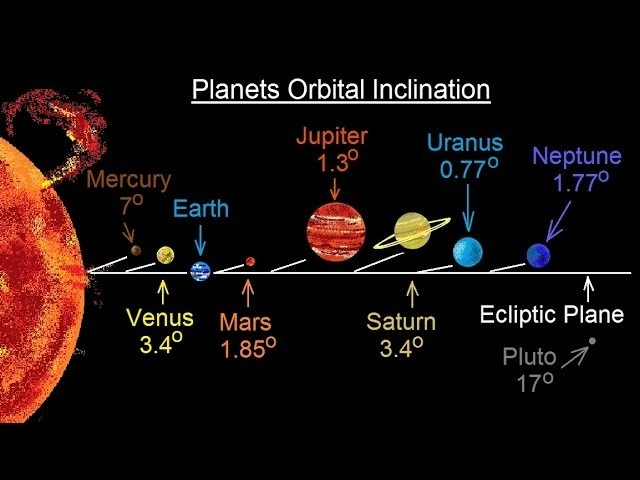
27 3月 2025Our Solar System exhibits a flat architecture, with nearly all planets orbiting within the same plane. Among them, Mercury is the most inclined planet with a mutual inclination of 7 degrees relative to Earth’s orbital plane (Figure 1). Mutual inclination, which refers to the angle between the orbital planes of two planets, serves as a key indicator of the dynamical architecture of planetary sy...
阅读更多...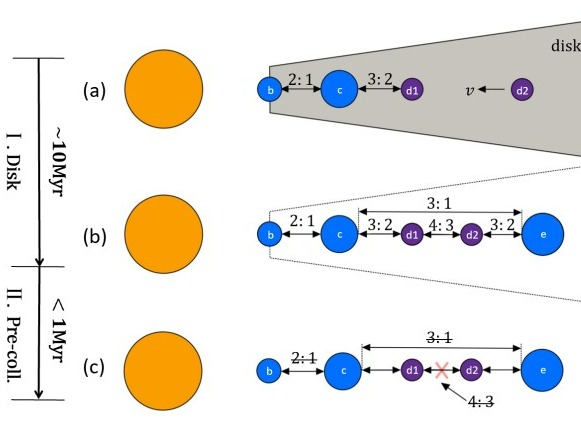
The Story of Kepler-221 -- A Broken Chain
19 3月 2025Kepler-221 is a G-type star hosting four planets. Among these planets, three of them -- b, c, and e – have their orbits following a rhythm known as a three-body resonance. This means that their orbital periods are close to integer, which resembles synchronized dancers following the same beat. For every six orbits of planet b, planet c completes three, and planet e completes one. But there’s a...
阅读更多...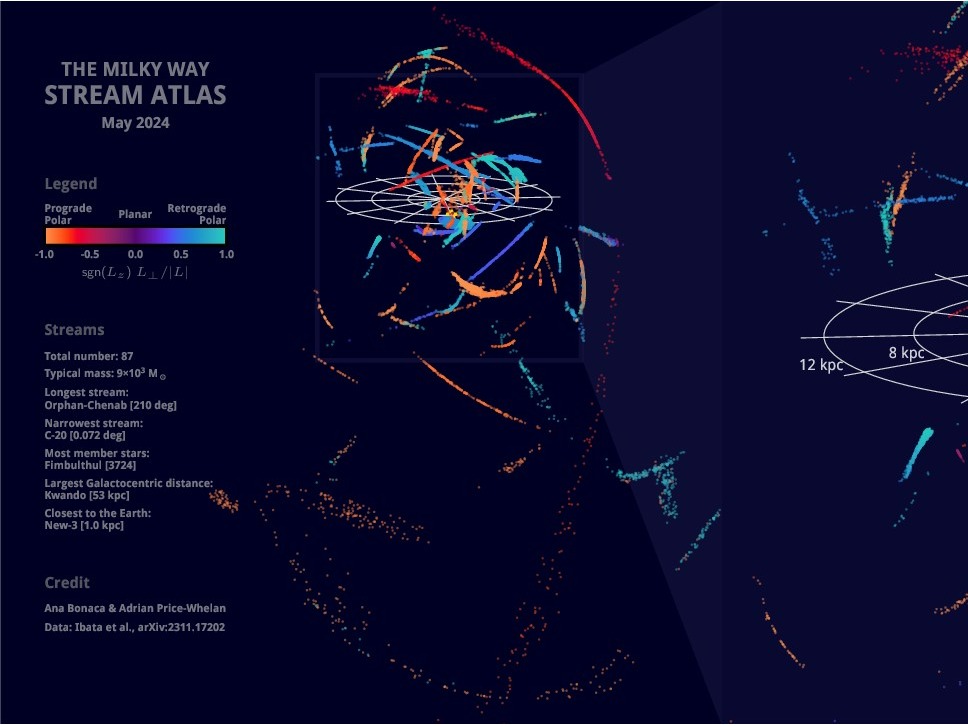
First Direct Measurements of Globular Cluster Mass Loss Through Stellar Streams
25 2月 2025Globular clusters are dense, ancient groups of stars orbiting galaxies like the Milky Way, often containing hundreds of thousands to even several million stars. Over billions of years, these clusters gradually lose mass due to two-body relaxation and tidal stripping. This slow unraveling process can eventually cause some clusters to dissolve entirely, contributing their stars to the galaxy's ha...
阅读更多...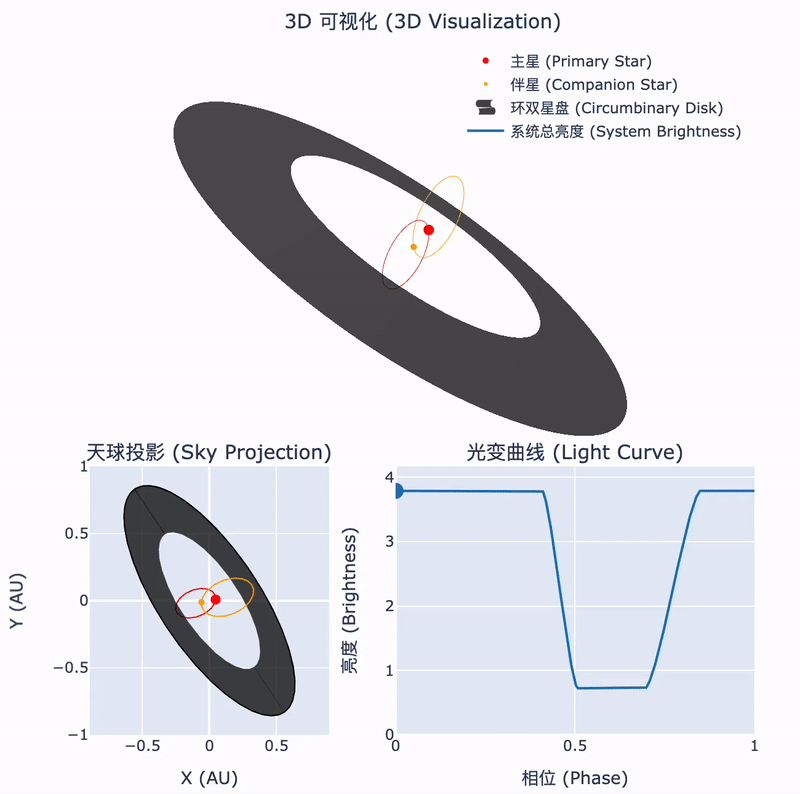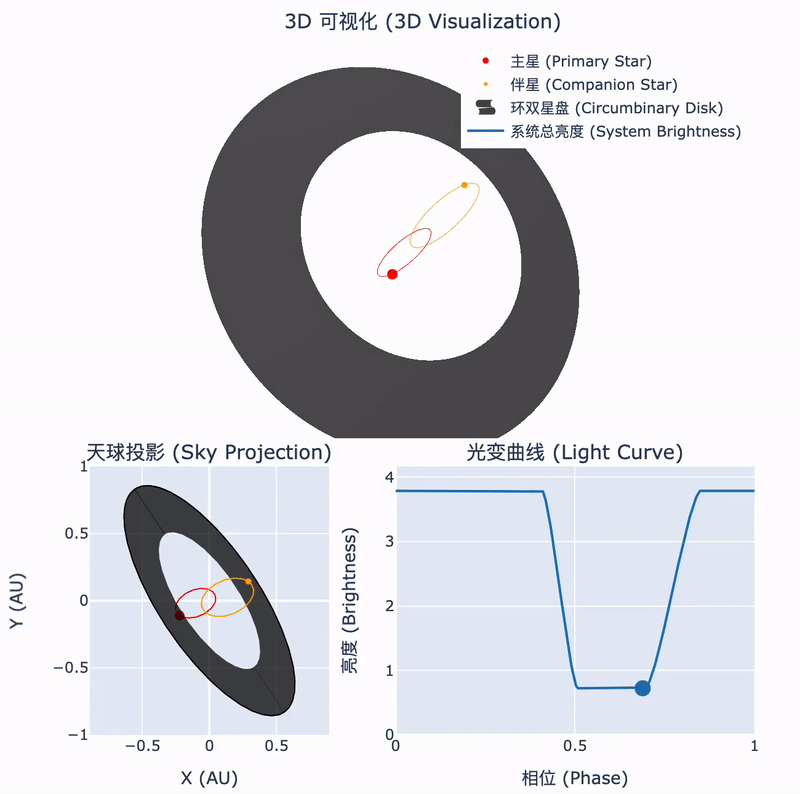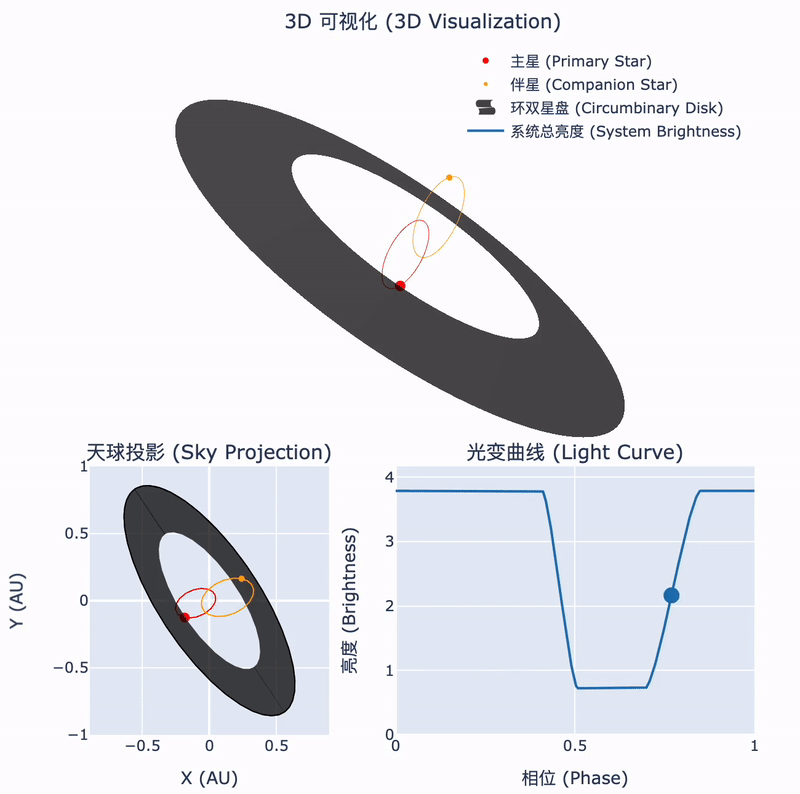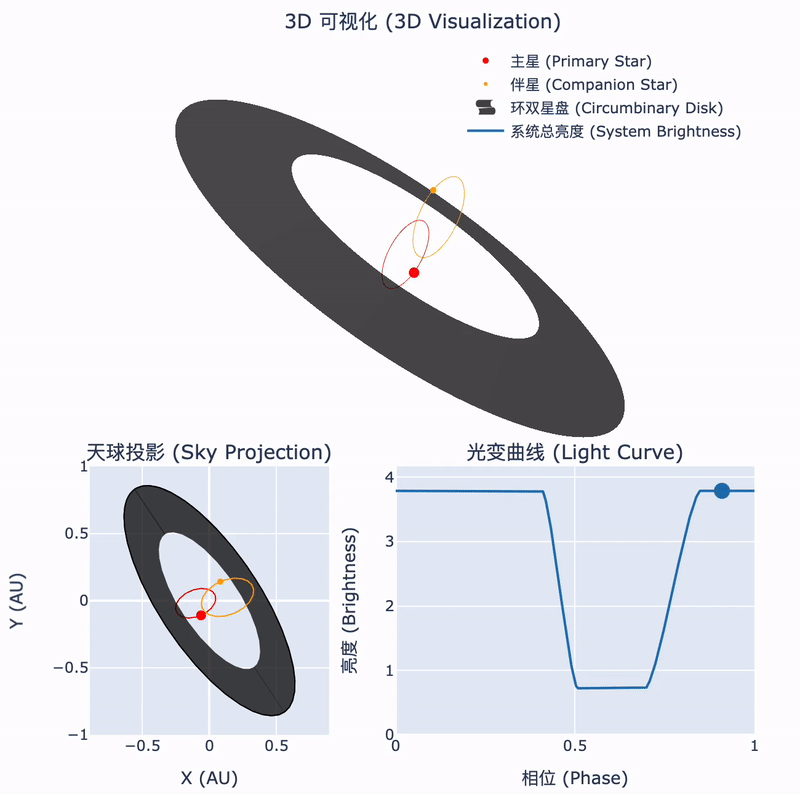
Tsinghua astronomers confirm the nature of a rare stellar system
30 12月 2024During the collapse of a molecular cloud into stars, some of the remaining material forms a circumstellar disk. In binary systems, this disk may surround the orbits of both stars. The interactions between such a circumbinary disk and the central binary can lead to fascinating astrophysical phenomena. Recently, an international team led by Tsinghua astronomers has identified such a unique object...
阅读更多...
An extremely low-density planet spins slow
05 12月 2024Planets are not perfect spheres. For example, Jupiter's equatorial radius is larger than its polar radius by 7%, and this aspherical shape is due to the fast spin of Jupiter, as one day on Jupiter is only 10 hr long. The shape of a planet therefore provides a measure of the rate and the orientation of its spin, which are ultimately related to the formation and evolution history of the planet as...
阅读更多...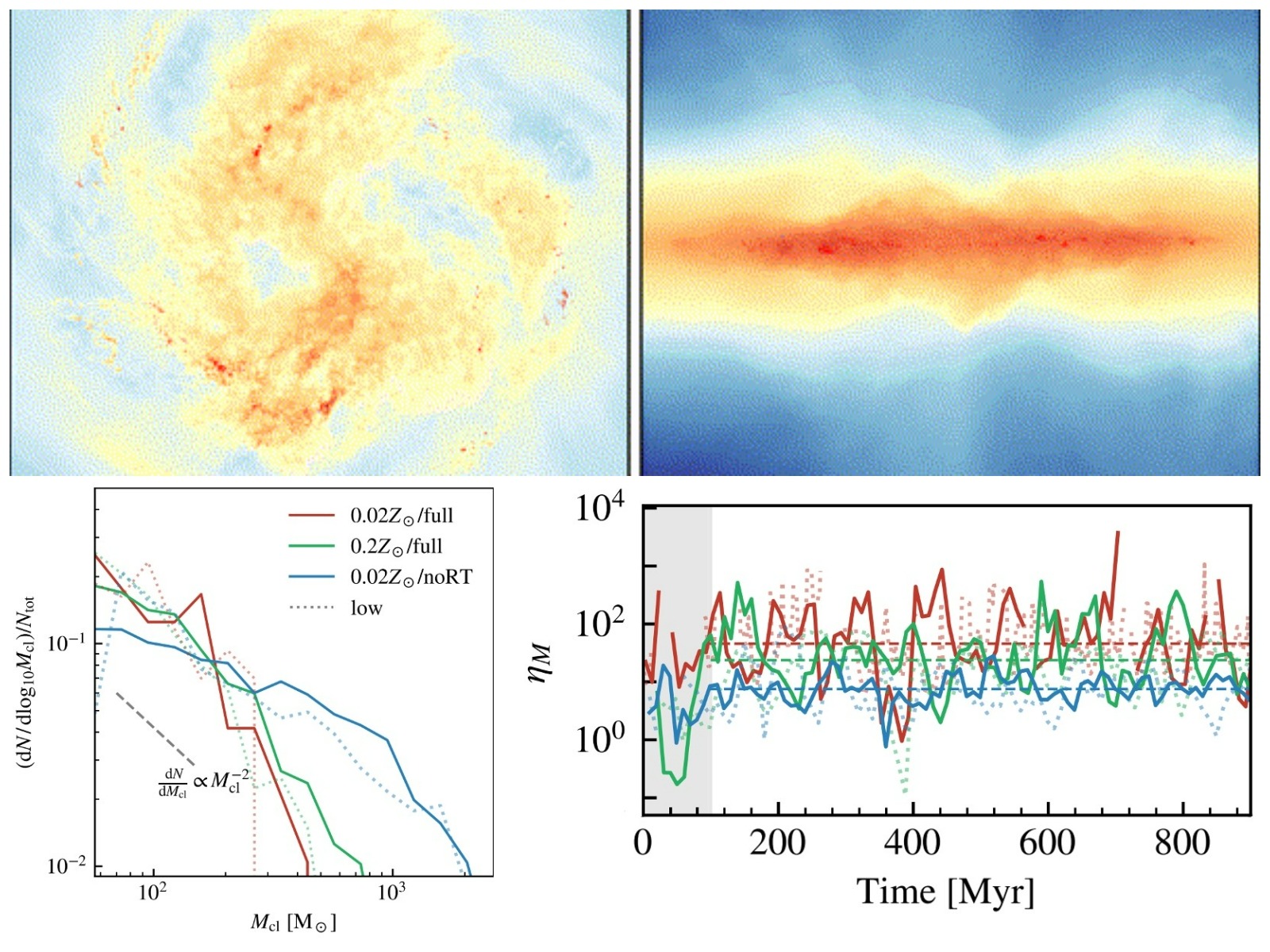
Revealing the nonlinear coupling between small-scale star formation and the large-scale galaxy ecosystem in RIGEL simulations
26 11月 2024Dwarf galaxies are the smallest, most numerous, and most abundant galaxies in the universe, making them an essential component of the cosmic ecosystem. Over the past decade, observations of the nearby universe have revealed a multitude of diverse and peculiar dwarf galaxies, whose formation and evolution remain one of the most enigmatic puzzles in galaxy formation. Due to their low mass and sha...
阅读更多...


