Research Highlights

A Hyperactive Fast Radio Burst in a “Clean” Environment
08 11月 2024The Greenbank Telescope and the related research highlight report can be found @ https://greenbankobservatory.org/news/u-s-national-science-foundation-green-bank-telescope-records-fastest-fast-radio-burst-yet/ Fast radio bursts (FRB) are intense radio transients from deep space, lasting only a few milliseconds. These bursts release an extraordinary amount of energy, with a single burst able to ...
阅读更多...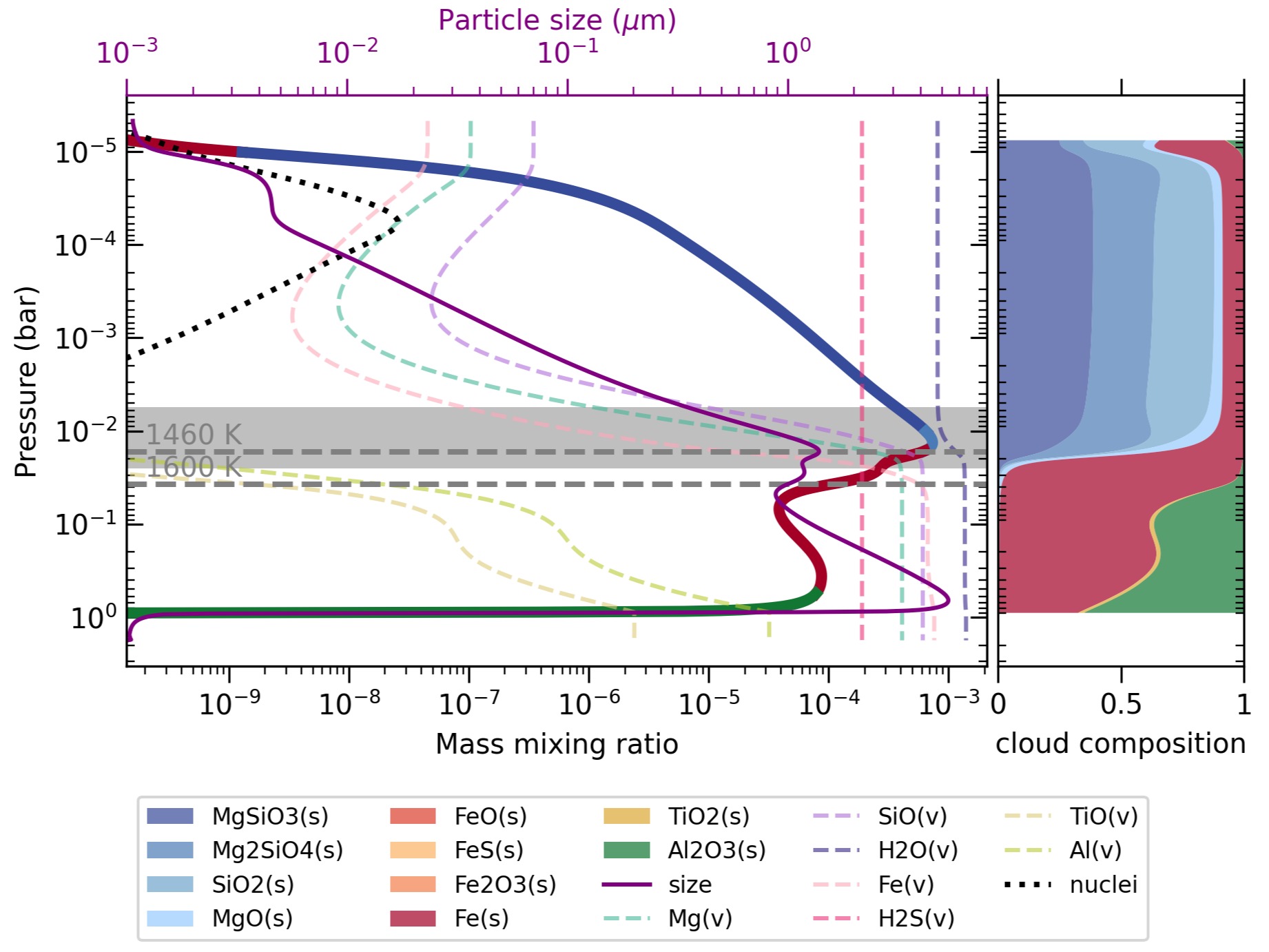
Understanding the composition of clouds on exoplanets
21 10月 2024Exoplanet's atmosphere contains the information where the planet is formed and how it accretes and evolves. Probing the atmosphere from the molecular lines in the transmission and emission spectrum unveils the chemical composition of the planet. However, an uncertain factor in retrieving exoplanet spectra is the presence of clouds. Clouds affect the transmission and emission spectrum by smearin...
阅读更多...
A Two-Earth-mass Planet Found Orbiting a Dead “Sun”
27 9月 2024Images of the area of the microlensing event, indicated by perpendicular white lines two weeks after peak magnification of the background star in 2020, taken by CFHT with seeing of ~ 0.5 arcsec (Left) and in 2023 after its disappearance, obtained by Keck-II with seeing of ~0.08 arcsec (Right). The planetary system with a white dwarf, a two-Earth-mass planet and brown dwarf cannot be seen; the p...
阅读更多...
JWST and VLT search for the signature of the First Stars
18 4月 2024The first stars, known as Population III stars, were born approximately 100 million years after the Big Bang when the universe was less than 1% of its present age. Population III stars are of fundamental importance to the initial mass function (IMF) of stars, which determines how the universe has evolved over time (see Fig. 1). As Population III stars are shortly lived, they rapidly enrich the ...
阅读更多...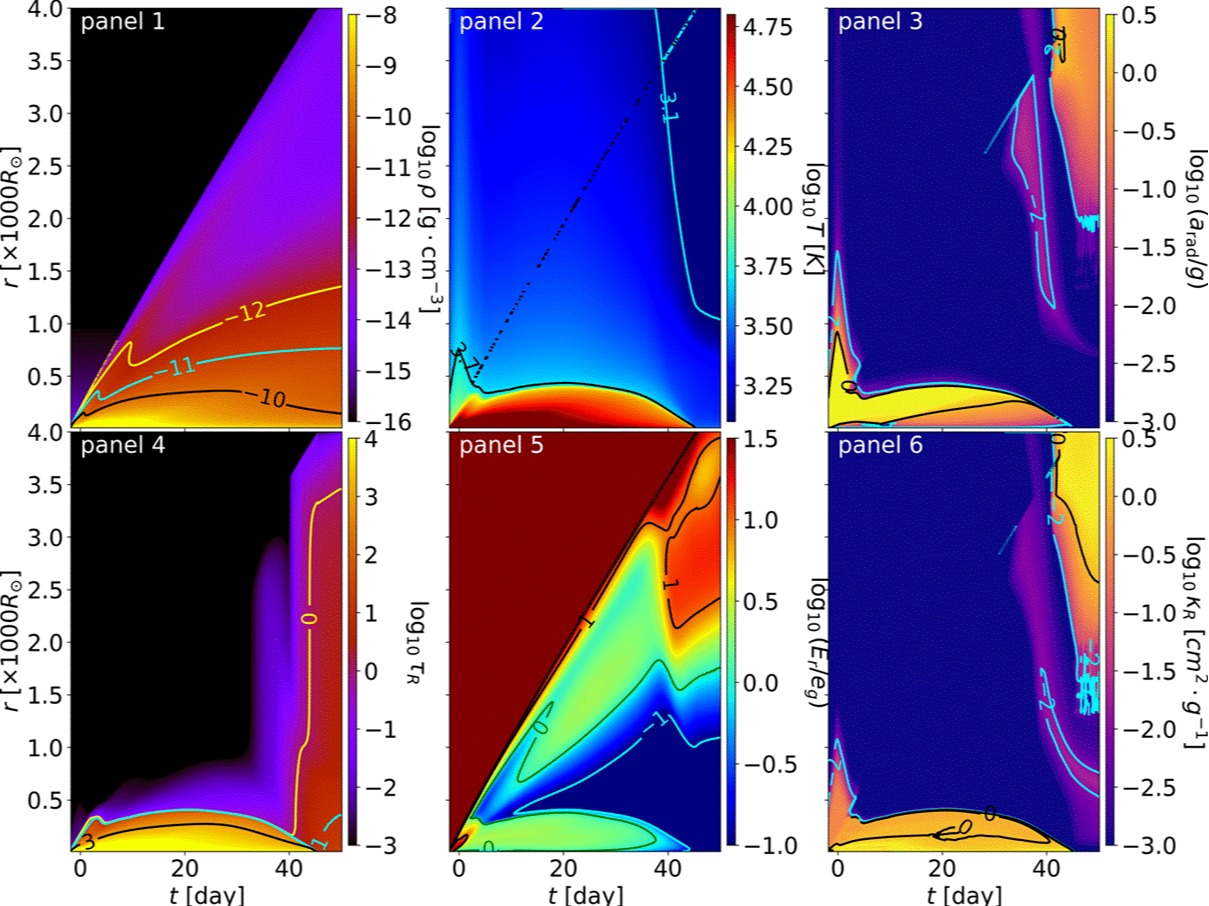
Bridging the Gap between Luminous Red Novae and Common Envelope Evolution
17 4月 2024Luminous red novae (LRNe) and common envelope evolution (CEE) are closely related astrophysical phenomena and evolutionary processes that are not well understood. Among them, CEE is a crucial stage in binary stellar evolution. Close compact binaries, Type Ia supernovae, hot sub-dwarfs, and gravitational wave sources may all be the product of CEE. On the other hand, LRNe are bright transients wi...
阅读更多...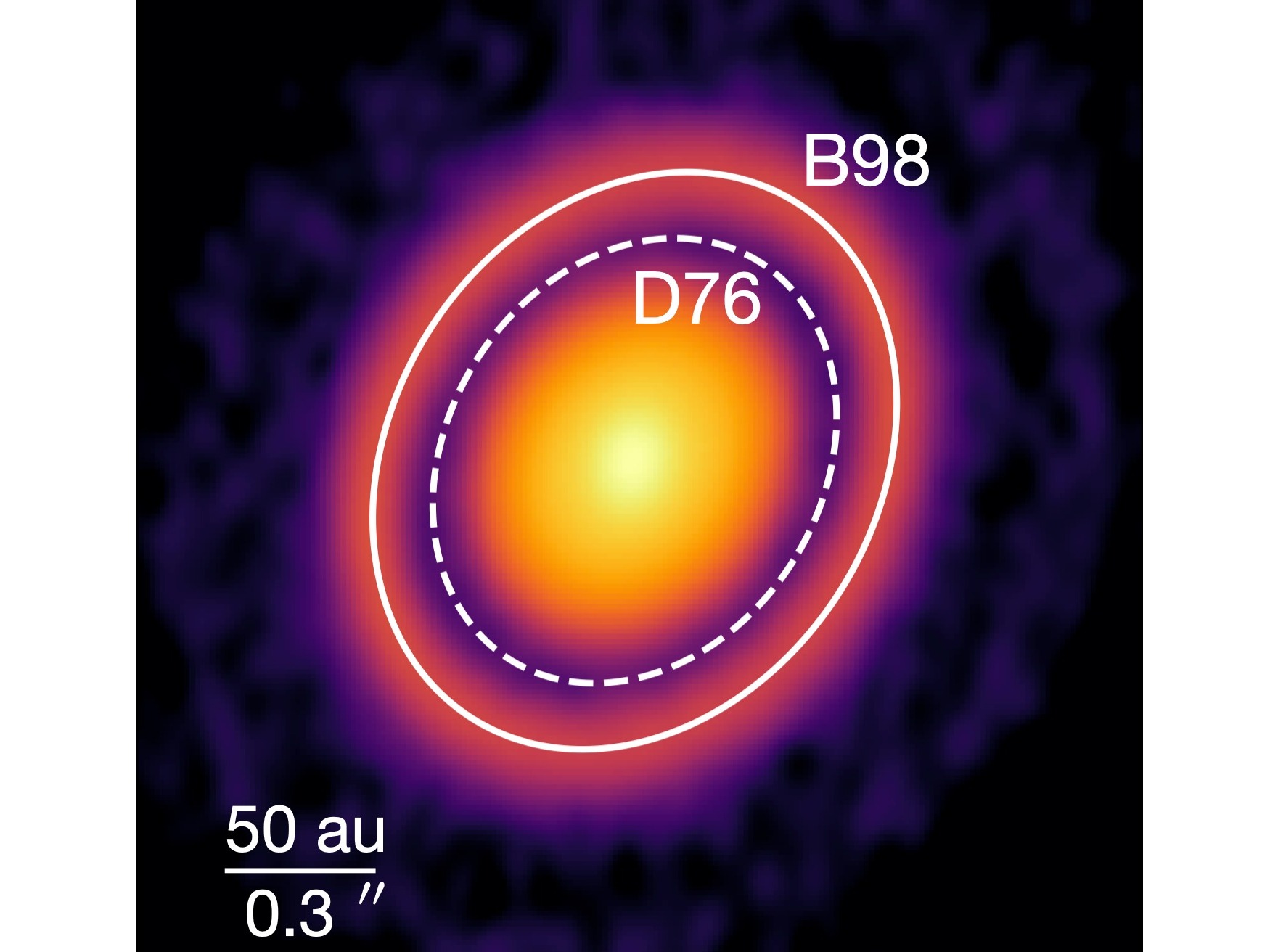
Accreting Planets Leave Chemical Footprints in Protoplanetary Disks
28 8月 2023Protoplanetary disks serve as the cradles of planet formation, often revealing captivating features such as bright rings and dark gaps in both dust continuum and gas emission maps. These features have traditionally been attributed planets, which shape the disk by gap-opening and altering its rotation profiles, effects that can potentially be observed.A new study led by Tsinghua Department of As...
阅读更多...


