极光计划X射线偏振探测器在轨工作两周年
2020年10月29日,由清华大学主导的空间天文项目“极光计划”成功实现了在轨工作两周年。2018年10月29日,装载“极光计划”的“铜川1号”立方星在酒泉卫星发射中心发射入轨;同年12月18日,“极光计划”探测到首光事例;2019年3月,在完成了卫星调试之后,“极光计划”全面进入科学观测阶段,先后对蟹状星云和天蝎座X-1开展了X射线偏振测量,同时对在轨本底进行观测研究。探测器至今工作正常,没有发现性能衰减。
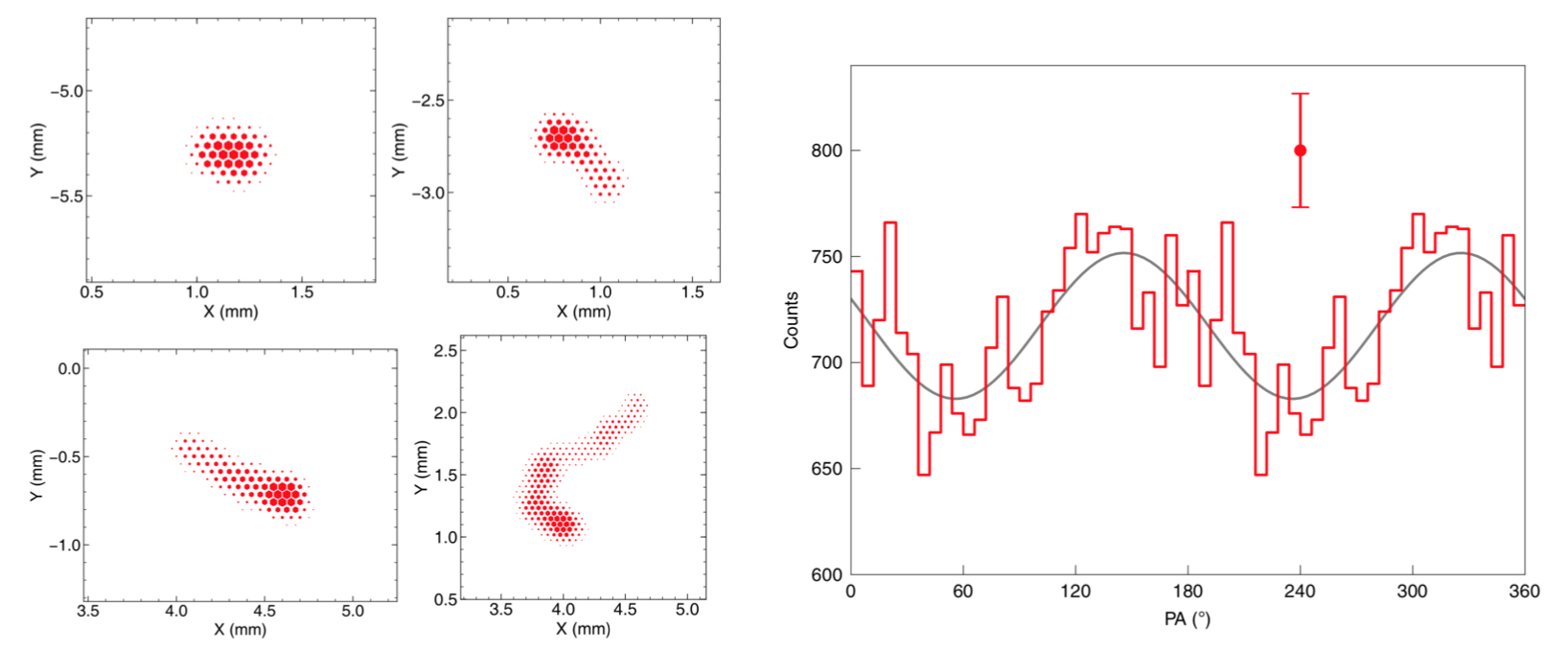
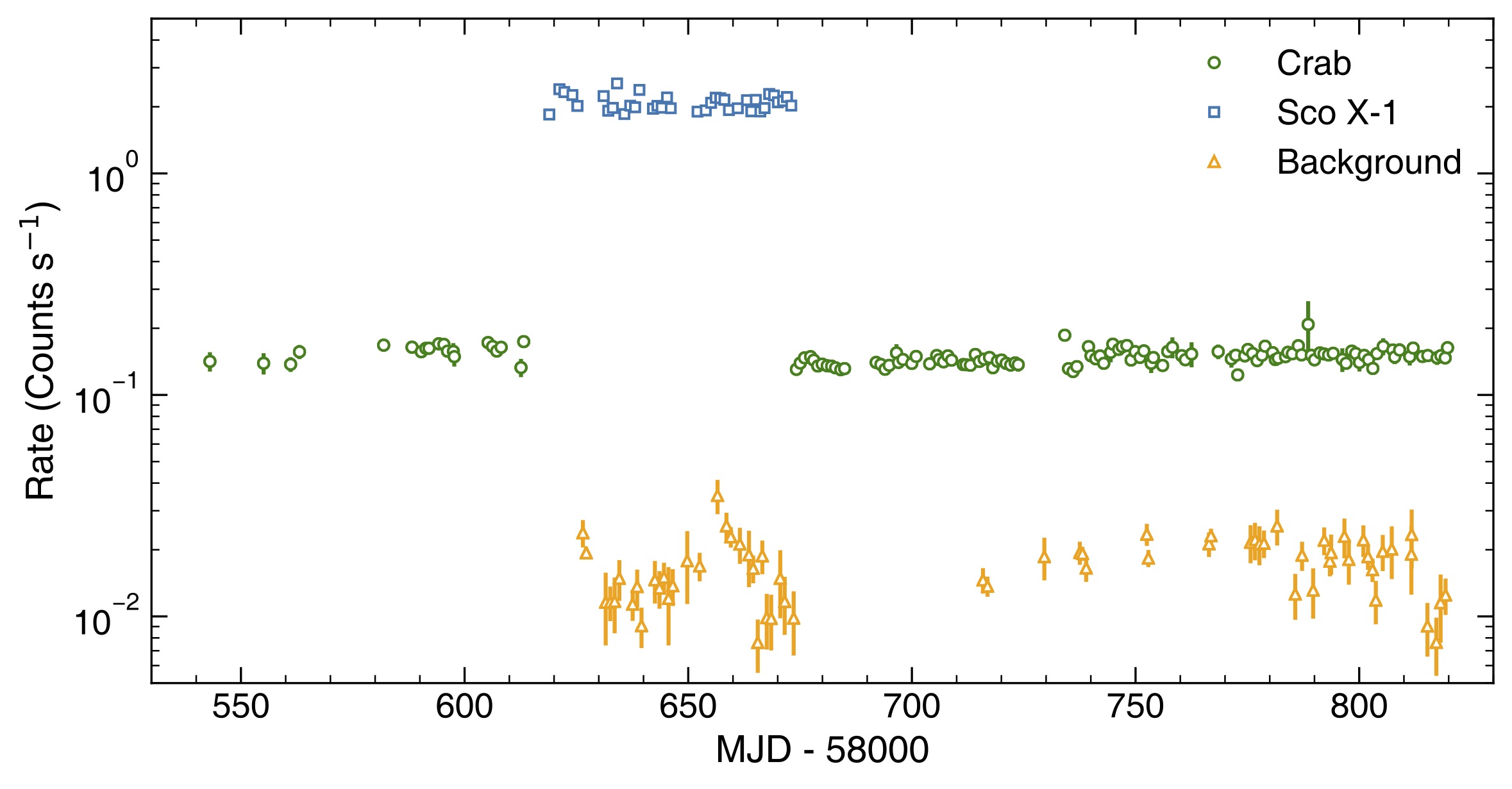
经过长期监测,“极光计划”探测到了蟹状星云的X射线偏振信号(图1),并发现了脉冲星偏振状态在自旋突变后会发生改变。近日,探测器在轨运行和性能状态的文章被《Advances in Space Research》杂志接收发表(图2)。此文也讨论总结了如何基于低成本、多载荷共享的立方星开展空间科学观测、新技术验证、学生培养等工作。
“极光计划”的成功运行,验证了基于光电效应的新一代X射线偏振探测方法的空间可用性,标志着由于技术困难停滞了40多年的天文软X射线偏振探测窗口重新开启,同时证明了立方星在空间天文中的价值。
迄今为止,基于“极光计划”的测试和观测数据已经发表了4篇文章:
- PolarLight: a CubeSat X-ray polarimeter based on the gas pixel detector, Feng, H., Jiang, W., Minuti, M. et al. 2019, Experimental Astronomy, 47, 225
- Re-detection and a possible time variation of soft X-ray polarization from the Crab, Feng, H., Li, H., Long, X. et al. 2020, Nature Astronomy, 4, 511
- The X-ray polarimetry window reopens, Feng, H., and Bellazzini, R. 2020, Nature Astronomy, 4, 547
- In-orbit Operation and Performance of the CubeSat Soft X-ray Polarimeter PolarLight, Li, H., Long, X., Feng, H. et al. 2020, accepted for publication in Advances in Space Research