
-
2025.02.25
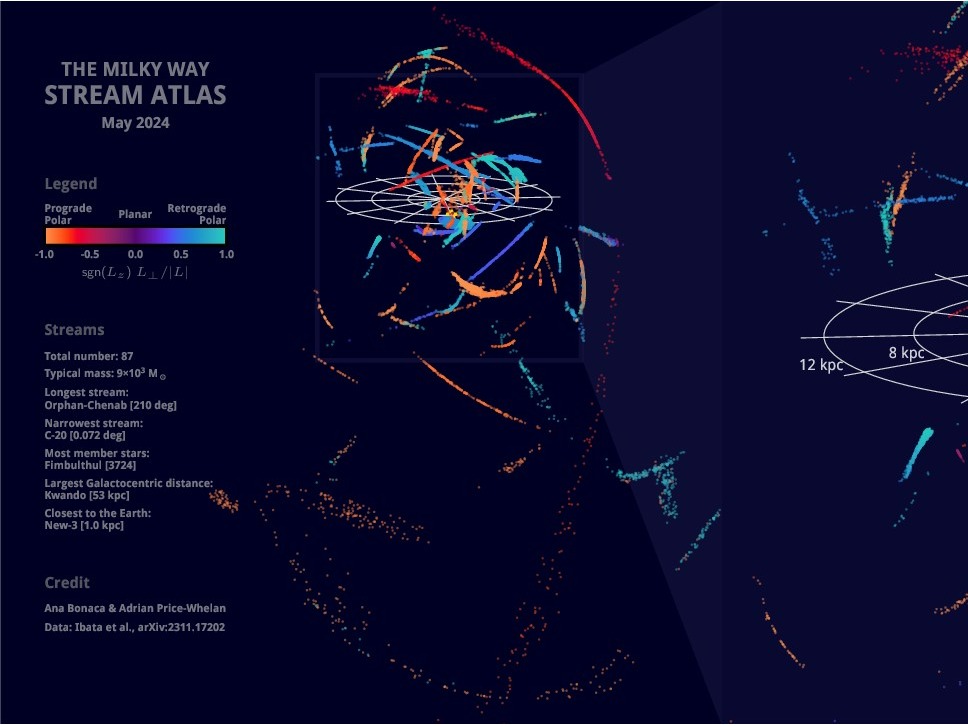
First Direct Measurements of Globular Cluster Mass Loss Through Stellar Streams
Globular clusters are dense, ancient groups of stars orbiting galaxies like the Milky Way, often containing hundreds of thousands to even several million stars. Over billions of years, these clusters gradually lose mass due to two-body relaxation and tidal stripping. This slow unraveling process can eventually cause some clusters to dissolve entirely, contributing their stars to the galaxy's ha...
More -
2024.12.30
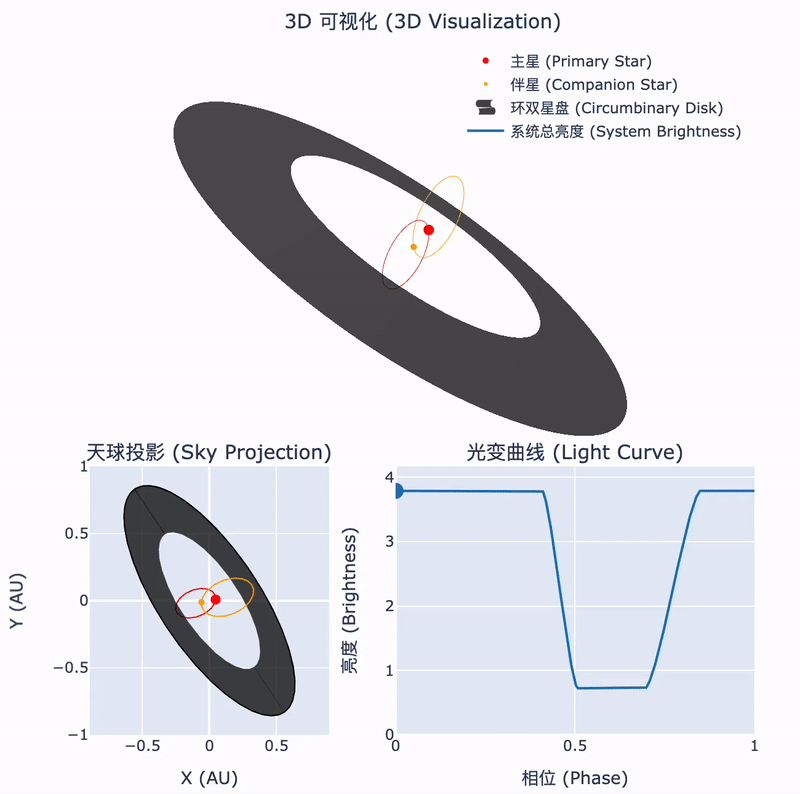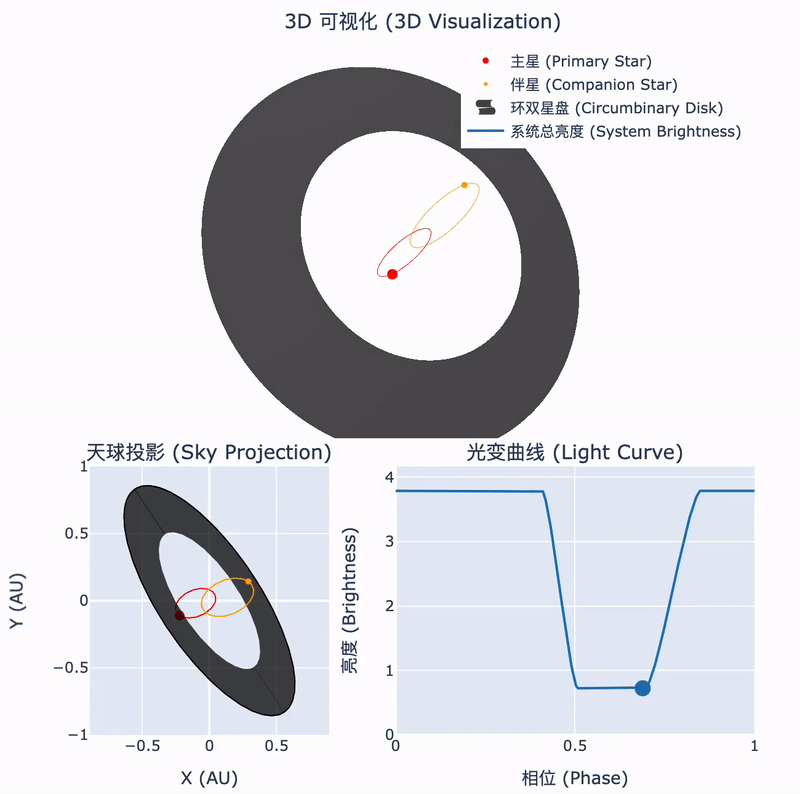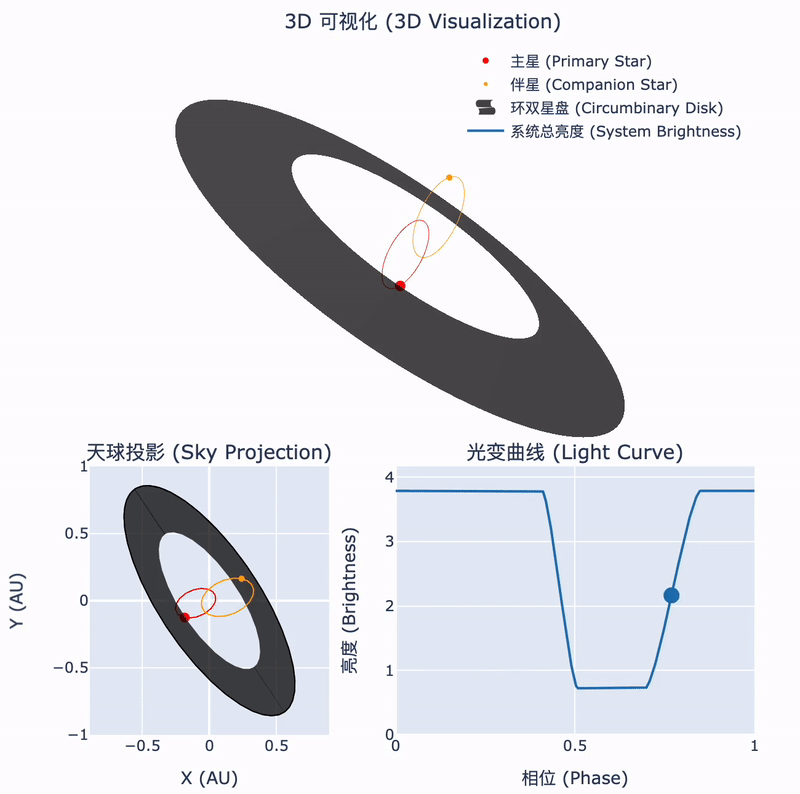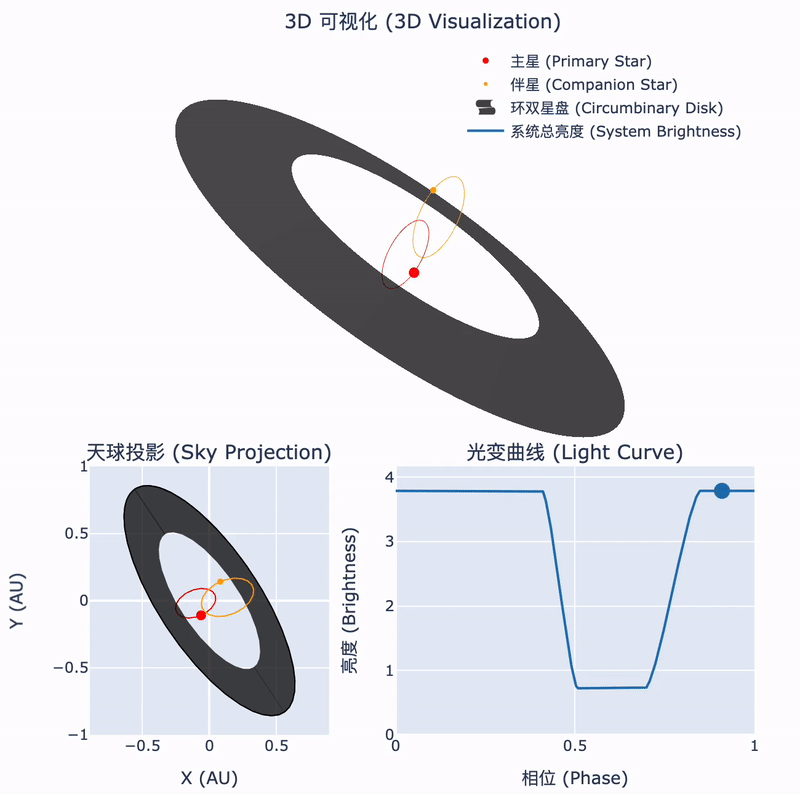
Tsinghua astronomers confirm the nature of a rare stellar system
During the collapse of a molecular cloud into stars, some of the remaining material forms a circumstellar disk. In binary systems, this disk may surround the orbits of both stars. The interactions between such a circumbinary disk and the central binary can lead to fascinating astrophysical phenomena. Recently, an international team led by Tsinghua astronomers has identified such a unique object...
More -

2024.12.05
An extremely low-density planet spins slow
Planets are not perfect spheres. For example, Jupiter's equatorial radius is larger than its polar radius by 7%, and this aspherical shape is due to the fast spin of Jupiter, as one day on Jupiter is only 10 hr long. The shape of a planet therefore provides a measure of the rate and the orientation of its spin, which are ultimately related to the formation and evolution history of the planet as...
More -
2024.11.26
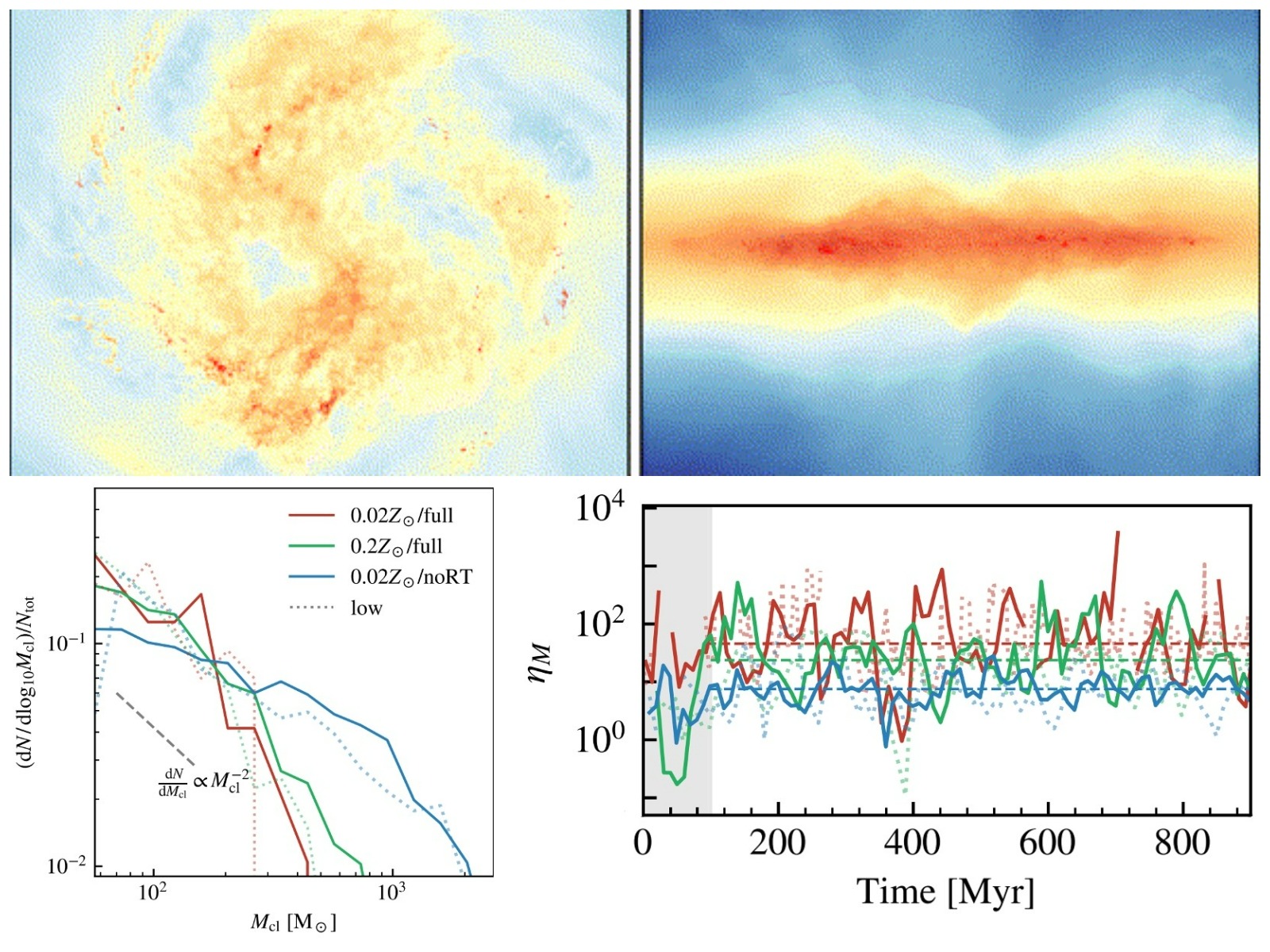
Revealing the nonlinear coupling between small-scale star formation and the large-scale galaxy ecosystem in RIGEL simulations
Dwarf galaxies are the smallest, most numerous, and most abundant galaxies in the universe, making them an essential component of the cosmic ecosystem. Over the past decade, observations of the nearby universe have revealed a multitude of diverse and peculiar dwarf galaxies, whose formation and evolution remain one of the most enigmatic puzzles in galaxy formation. Due to their low mass and sha...
More -

2024.11.08
A Hyperactive Fast Radio Burst in a “Clean” Environment
The Greenbank Telescope and the related research highlight report can be found @ https://greenbankobservatory.org/news/u-s-national-science-foundation-green-bank-telescope-records-fastest-fast-radio-burst-yet/ Fast radio bursts (FRB) are intense radio transients from deep space, lasting only a few milliseconds. These bursts release an extraordinary amount of energy, with a single burst able to ...
More



